How to Perform Technical Analysis on Supermicro Computer Inc. (SMCI) Using Python and yfinance
2024-06-08
Introduction to Technical Analysis and yfinance
In today’s fast-paced financial world, staying ahead with insightful analysis is crucial. Python's yfinance library offers an accessible and efficient way to download and analyze historical market data from Yahoo Finance. Whether you're a seasoned analyst or a beginner, yfinance simplifies the process of obtaining stock prices, financial metrics, and historical data, all for free. In this guide, we’ll focus on how to use yfinance to perform a technical analysis on Supermicro Computer Inc. (SMCI), a leading provider of high-performance server technology.
Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis
Before diving into the technical analysis, let’s briefly differentiate between the two main types of stock analysis:
- Fundamental Analysis: Evaluates a stock's intrinsic value based on economic, financial, and other qualitative and quantitative factors. It includes analyzing financial statements, company management, and market conditions.
- Technical Analysis: Focuses on analyzing past trading activity and price movements using statistical tools and charts. It identifies patterns and trends that may predict future price movements.
For a holistic investment strategy, combining both analyses can provide a more comprehensive view.
Setting Up Your Python Environment
To get started, you need Python installed on your system. We'll also require the following libraries: yfinance, pandas, and matplotlib. You can install these using pip:
pip install yfinance pandas matplotlibFetching Historical Data for SMCI
Using the yfinance library, you can easily download historical stock data for SMCI. The process is straightforward, allowing you to access a wealth of financial data without the need for costly data services. Here's how you can fetch the data:
import yfinance as yf
# Fetch historical data for SMCI
symbol = 'SMCI'
data = yf.download(symbol, start='2023-01-01', end='2024-06-06')
# Display the first few rows of the data
print(data.head())
Calculating Key Technical Indicators
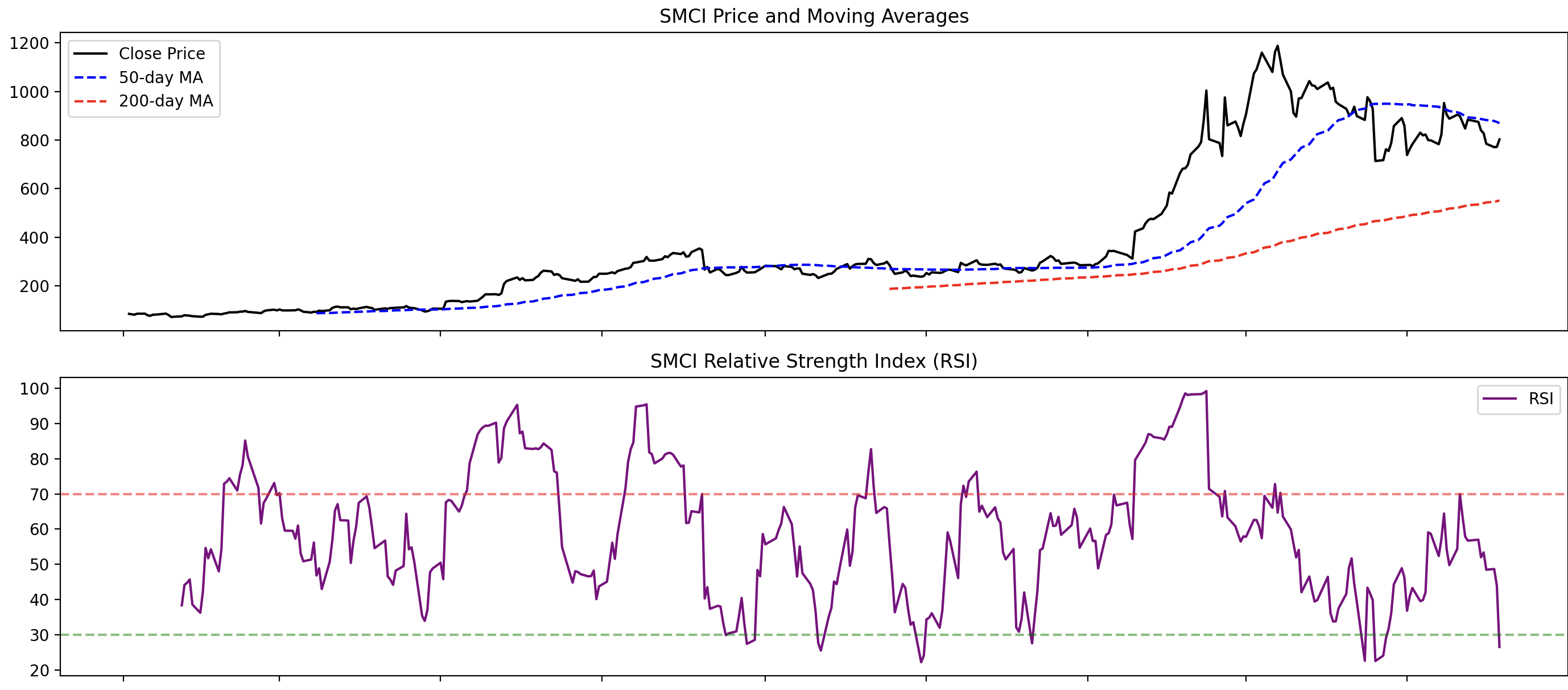
To perform a thorough technical analysis, we'll calculate several key indicators: Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
Moving Averages (SMA and EMA)
Moving Averages smooth out price data to help identify the trend direction. We’ll calculate both the Simple Moving Average (SMA) and the Exponential Moving Average (EMA):
# Calculate 50-day and 200-day moving averages
data['50_day_MA'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=50).mean()
data['200_day_MA'] = data['Close'].rolling(window=200).mean()
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements, helping to identify overbought or oversold conditions:
# Calculate RSI
delta = data['Close'].diff()
gain = (delta.where(delta > 0, 0)).rolling(window=14).mean()
loss = (-delta.where(delta < 0, 0)).rolling(window=14).mean()
rs = gain / loss
data['RSI'] = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator showing the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price:
# Calculate MACD
short_ema = data['Close'].ewm(span=12, adjust=False).mean()
long_ema = data['Close'].ewm(span=26, adjust=False).mean()
data['MACD'] = short_ema - long_ema
data['Signal'] = data['MACD'].ewm(span=9, adjust=False).mean()
Visualizing the Data
Visualizing the data helps in understanding trends and potential signals. We'll use matplotlib to plot the data:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Plot the data
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, figsize=(14, 10), sharex=True)
# Plot Closing price and Moving Averages
ax[0].plot(data['Close'], label='Close Price', color='black')
ax[0].plot(data['50_day_MA'], label='50-day MA', color='blue', linestyle='--')
ax[0].plot(data['200_day_MA'], label='200-day MA', color='red', linestyle='--')
ax[0].set_title(f'{symbol} Price and Moving Averages')
ax[0].legend()
# Plot RSI
ax[1].plot(data['RSI'], label='RSI', color='purple')
ax[1].axhline(70, linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, color='red')
ax[1].axhline(30, linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, color='green')
ax[1].set_title(f'{symbol} Relative Strength Index (RSI)')
ax[1].legend()
# Plot MACD
ax[2].plot(data['MACD'], label='MACD', color='blue')
ax[2].plot(data['Signal'], label='Signal Line', color='red', linestyle='--')
ax[2].set_title(f'{symbol} MACD')
ax[2].legend()
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Interpreting the Results
By analyzing the generated charts, you can interpret the indicators as follows:
- Price and Moving Averages: If the price is above the 200-day MA, it indicates a long-term bullish trend. Conversely, if it nears the 50-day MA, it could signal potential short-term consolidation or weakness.
- RSI: RSI values close to 30 suggest the stock might be oversold and could be due for a rebound if the price stabilizes or rises.
- MACD: If the MACD is below the Signal line, it indicates bearish momentum. Potential buyers should watch for a reversal or stabilization of this indicator.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Performing technical analysis using Python and yfinance provides a robust way to evaluate stock performance without incurring high costs. By following the steps in this guide, you can gain valuable insights into price trends and potential signals for Supermicro Computer Inc. (SMCI) or any other stock.
Key Takeaways:
- Combine technical analysis with fundamental analysis and market knowledge for comprehensive insights.
- Use multiple indicators to confirm trends and signals.
- Stay informed about market news and events that could impact stock performance.
For a comprehensive view combining both technical and fundamental insights, you can also check out our detailed analysis for SMCI.


